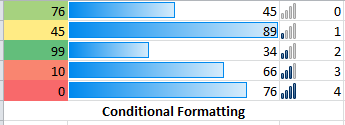
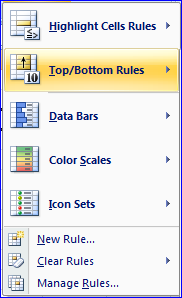
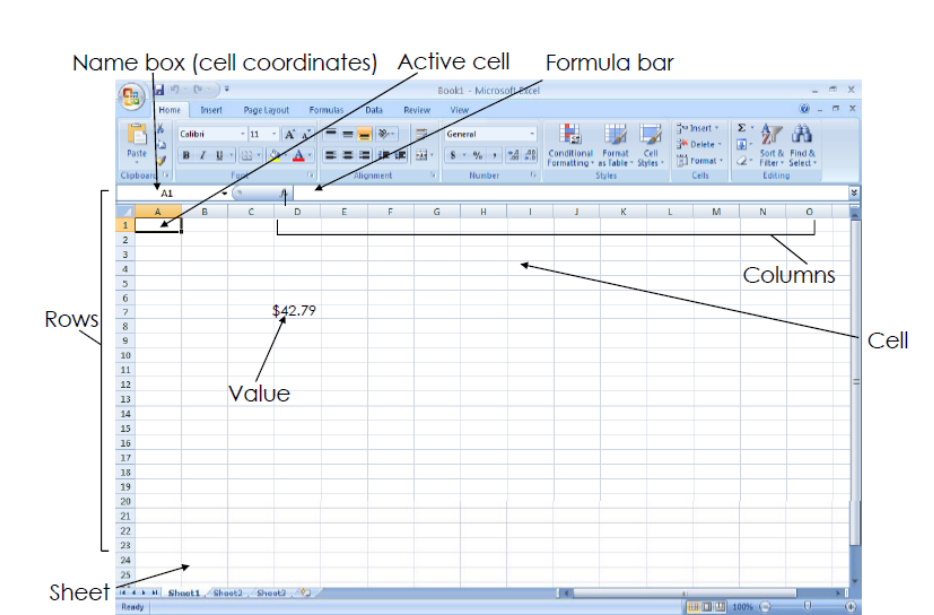
Errors
1. #### - the cell contains a number too long for the cell
2. #DIV/0 - the cell contains a formula that divides a value by 0
3. #N/A - there is a missing data or found no match
4. #NAME? - undefined name range or cell name
5. #NULL! - 2 ranges doesn't intersect. This usually happens when the cell references are separated by a space and not by a comma, operator, or colon
6. #NUM! - used an invalid argument to a function
7. #REF! - invalid cell reference
8. #VALUE! - argument for a function is of an incorrect data type
Reference: http://prajwaldesai.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/error-code.jpeg
http://moodle.pshs-brc.edu.ph/pluginfile.php/4746/mod_resource/content/0/Functions%20and%20Formula.pdf